Fertility is influenced by a wide range of factors, some of which you can change, and some you can’t. In Part 1 of this blog, we explored lifestyle and environmental factors that you can influence, such as diet, exercise, and sleep. In this second part, we’ll look at the factors that are outside of your control and explain what you can still do to protect or preserve your fertility.
Age
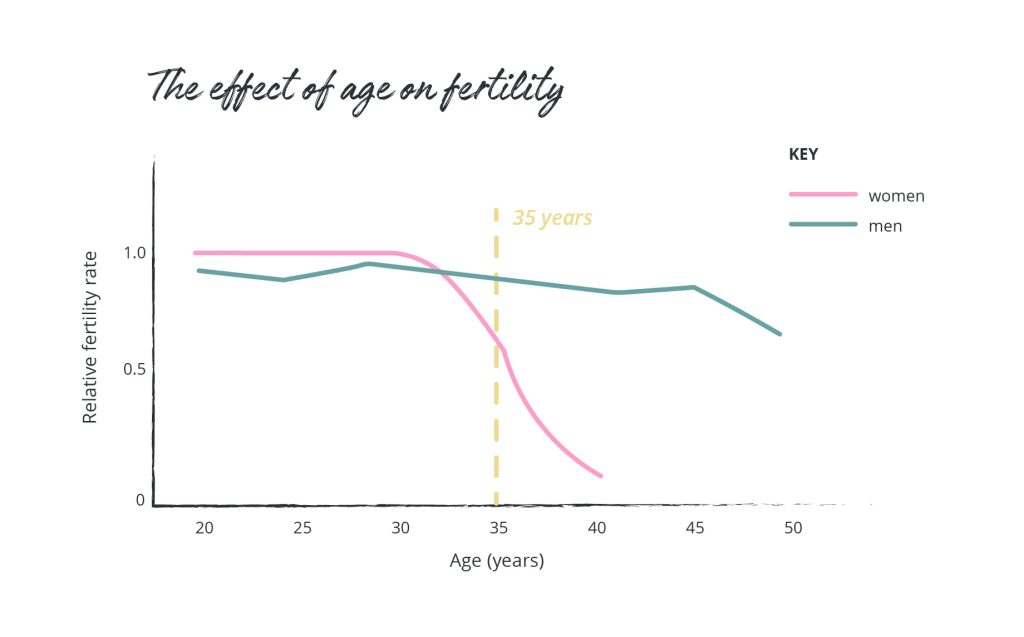
Age is the most important factor affecting fertility, especially for women.
- For women: Fertility begins to decline gradually in their early 30s, and more sharply after age 35. This happens because both the quantity and quality of eggs decrease with age. By the time a woman reaches 40, her chances of getting pregnant naturally are significantly lower, and the risk of miscarriage and other complications is higher.
- For men: While the decline is more gradual, age also affects fertility. Sperm quality (including the movement, shape, and DNA integrity of the sperm) can begin to decline as men get older. Older men are also more likely to experience reduced testosterone levels and erectile dysfunction, which can affect fertility.
Health Conditions, Medications, and Genetics
a) Health Conditions
In women, health conditions that affect fertility may include:
- Endometriosis, which can cause scarring and inflammation that affects the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common hormonal disorder that can affect ovulation.
- Thyroid issues, both overactive and underactive thyroid can disrupt menstrual cycles.
- Premature ovarian insufficiency, which is when the ovaries stop working properly before age 40.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), like chlamydia and gonorrhoea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, causing damage to reproductive organs.
- Other chronic conditions such as diabetes and autoimmune diseases can also impact fertility.

In men, common conditions that affect fertility include:
- Erectile dysfunction or ejaculatory disorders.
- Low testosterone levels.
- Varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum) can impair sperm production.
b) Medications
For women, medications that may impact fertility include:
- Long-term use of certain painkillers.
- Chemotherapy.
- Antipsychotic medicines.
- Medications for fluid retention.
For men, medications that may impact fertility include:
- Sulfasalazine (used for conditions such as Crohn’s disease or rheumatoid arthritis).
- Chemotherapy.
- Long-term use of anabolic steroids.
- Certain herbal remedies.
If you're planning to conceive, it’s important to speak to your doctor about whether your medications could affect your fertility.
c) Genetic Factors
Sometimes, fertility challenges run in families. If close relatives experienced the below conditions, you may be affected by these conditions as well:
- Early menopause (you may be at higher risk of having a reduced ovarian reserve).
- Chromosomal abnormalities or genetic conditions that affect egg or sperm quality.
- Sperm abnormalities, low sperm count, or sperm mobility issues.
While you can’t change your genes, being aware of your family’s medical history can help you make informed decisions earlier.
What Can You Do to Protect Your Fertility?
If you’re thinking about starting a family someday and are worried about how factors like age or health conditions might affect your chances, learning about your options for preserving your fertility is the best first step you can take.
Egg freezing (for women) and sperm freezing (for men) allow you to store your eggs or sperm at a younger age, when the quality is higher. These options don’t guarantee a successful pregnancy later, but they can increase your chances if you face age-related or medical fertility challenges when you start trying for children.
If you have a medical condition or a family history of fertility issues, it’s worth speaking to a fertility specialist to explore your options early.
Conclusion
While you can’t change your age or your genes, understanding how these factors influence fertility can help you to plan ahead. When you combine this knowledge with healthy lifestyle choices (covered in Part 1 of this blog), you give yourself the best possible chance of conceiving when the time is right for you.
Remember: Everyone’s fertility journey is different. If you have questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to talk to your general practitioner or a fertility specialist.
Being informed is the first step. Take a moment to explore our fertility preservation section (at the top of your screen) and start your journey today.





